
|
AROUND THE GLOBE |

|
AROUND THE GLOBE |
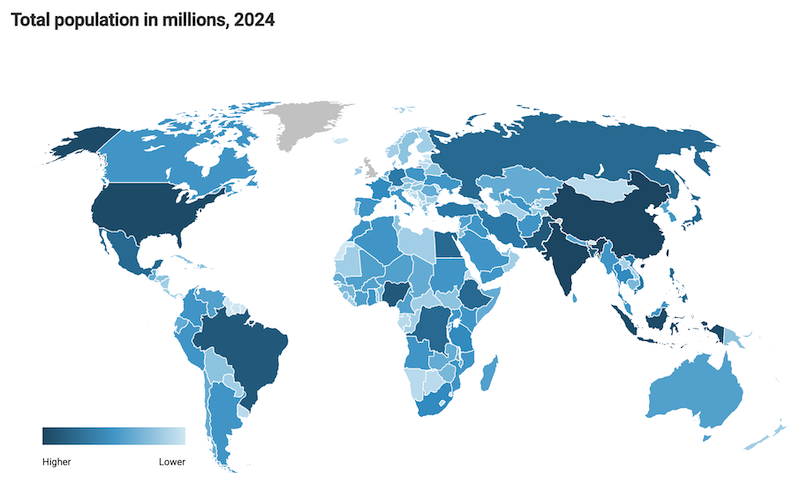 |
👫World Population MapAs of November 2024, the global population has reached approximately 8.19 billion, marking a consistent increase at an annual growth rate of around 0.85%. Asia remains the most densely populated continent, housing over 58% of the world's population, while Africa shows the fastest growth rate at 2.3%, indicating a significant future demographic shift as its population expands. Recently, India has surpassed China, becoming the most populous nation with over 1.44 billion people, reflecting broader trends in birth rates and urbanization. Daily, the world experiences around 361,765 births and 170,463 deaths, resulting in a net increase of approximately 190,000 people each day. This growth brings challenges, including the need for resources, environmental sustainability, and urban planning, as population dynamics drive economic and social policies globally. The regions differ notably, with some, like Europe, experiencing population decline, while others grow rapidly, reshaping the global landscape and demanding a careful balance between growth and sustainability. |
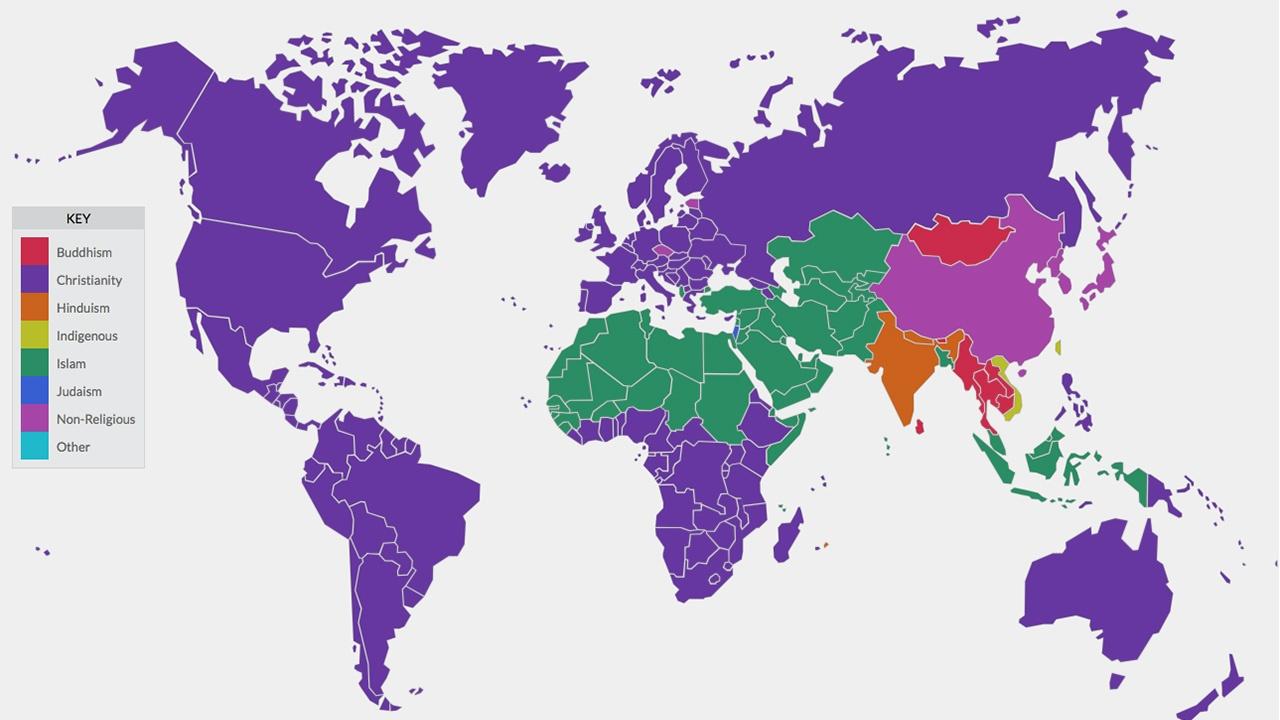
🪬World Religions MapChristianity is currently the world’s largest religion, with around 2.2 billion followers, constituting about 31% of the global population. Islam follows closely with about 1.6 billion adherents, representing 25% of the global population, and is projected to grow rapidly in the coming decades. Hinduism, with its roots in the Indian subcontinent, is the third-largest religion, encompassing roughly 15% of the world, mainly in India and Nepal. Buddhism, another major religion originating in Asia, has around 500 million followers, making up 6.6% of the global population. Smaller in global population but significant, Judaism has roughly 14 million adherents worldwide, comprising 0.2% of the population. Additionally, around 1.2 billion people, or 16%, identify as religiously unaffiliated, including atheists, agnostics, and those with no particular religious alignment, particularly concentrated in East Asia and parts of Europe. Traditional or folk religions and other faiths, including smaller groups like the Baha’i, Sikhism, and Jainism, account for the remainder. The global religious landscape continues to evolve due to demographic trends, particularly in regions with higher birth rates among religious populations. |
 |
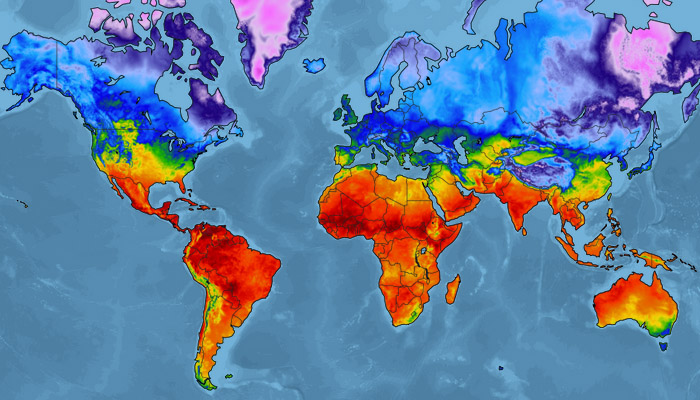 |
🌦️World Weather Map
In 2024, global weather patterns have continued to reveal a complex mix of extreme and record-breaking events. Average global temperatures have reached unprecedented highs, with El Niño further driving temperatures. January 2024 alone was the warmest on record, with a global surface temperature 1.27°C above the 20th-century average. This warming trend has resulted in extreme weather worldwide: severe heatwaves affected Asia and South America, with record-breaking temperatures in cities like Rio de Janeiro and numerous fatalities in parts of India and the Philippines. At the same time, major floods struck Brazil and Houston, while devastating wildfires continued in parts of Canada and other regions.
|
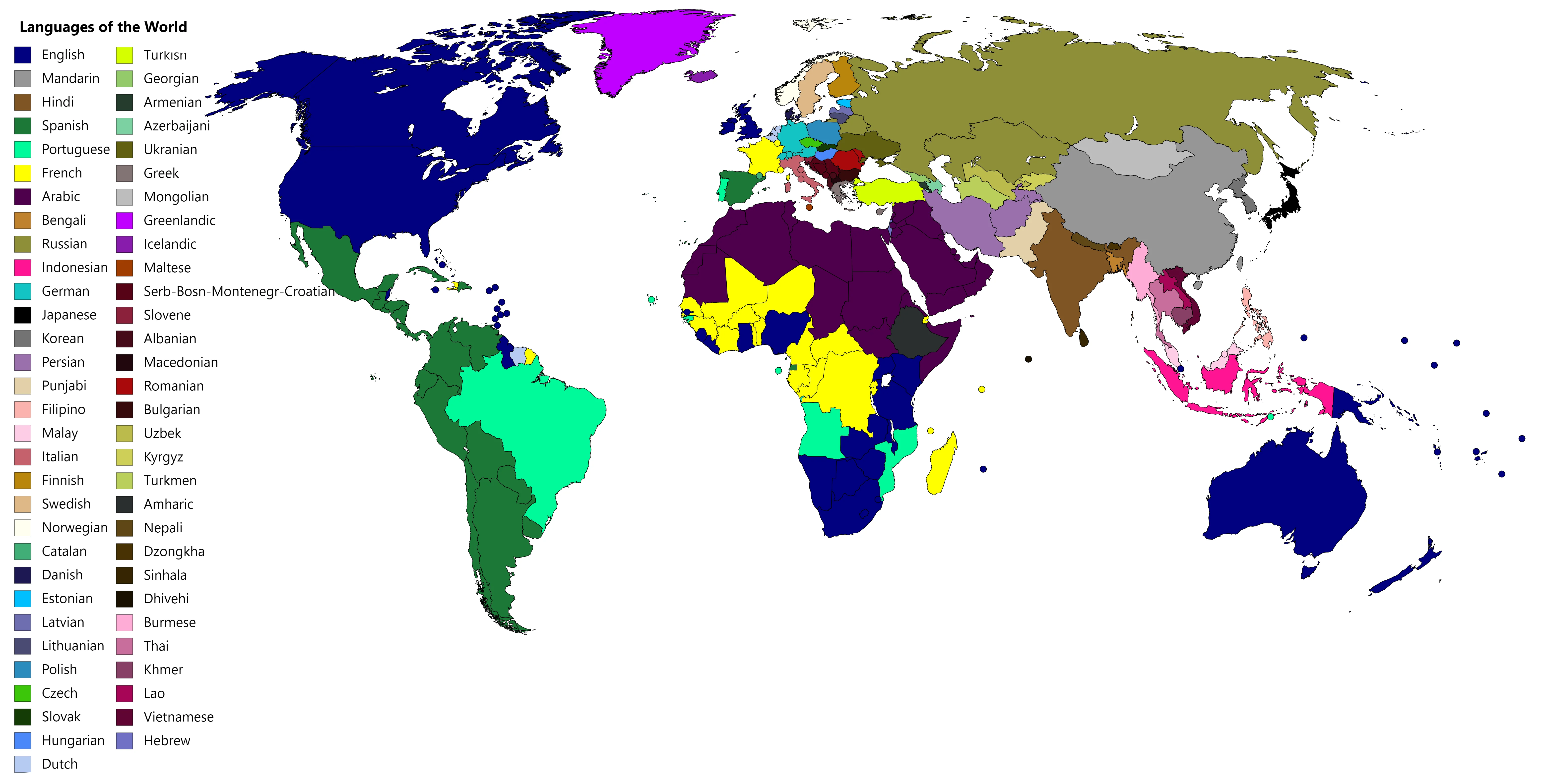
📕World Language MapLanguages in the world reflect immense cultural diversity, with the most widely spoken languages having millions of speakers across multiple countries. English leads as a global lingua franca with over 1.5 billion speakers, facilitating international business, science, and digital communication. Mandarin Chinese follows with approximately 1.1 billion native speakers, primarily in China, where its complex writing system and tonal pronunciation embody a rich cultural heritage. Hindi, spoken mainly in India, has around 608 million speakers, making it the third most widely spoken language, known for its expressive film and literary traditions. Spanish, spoken across Spain and much of Latin America, and Arabic, used widely in the Middle East and North Africa, each have hundreds of millions of speakers and extensive historical, religious, and literary significance. Other major languages include French, Bengali, Portuguese, Russian, and Urdu, each with unique cultural influences and significant speaker populations around the globe. The diversity of these languages highlights the range of human expression and connection across continents. |
 |
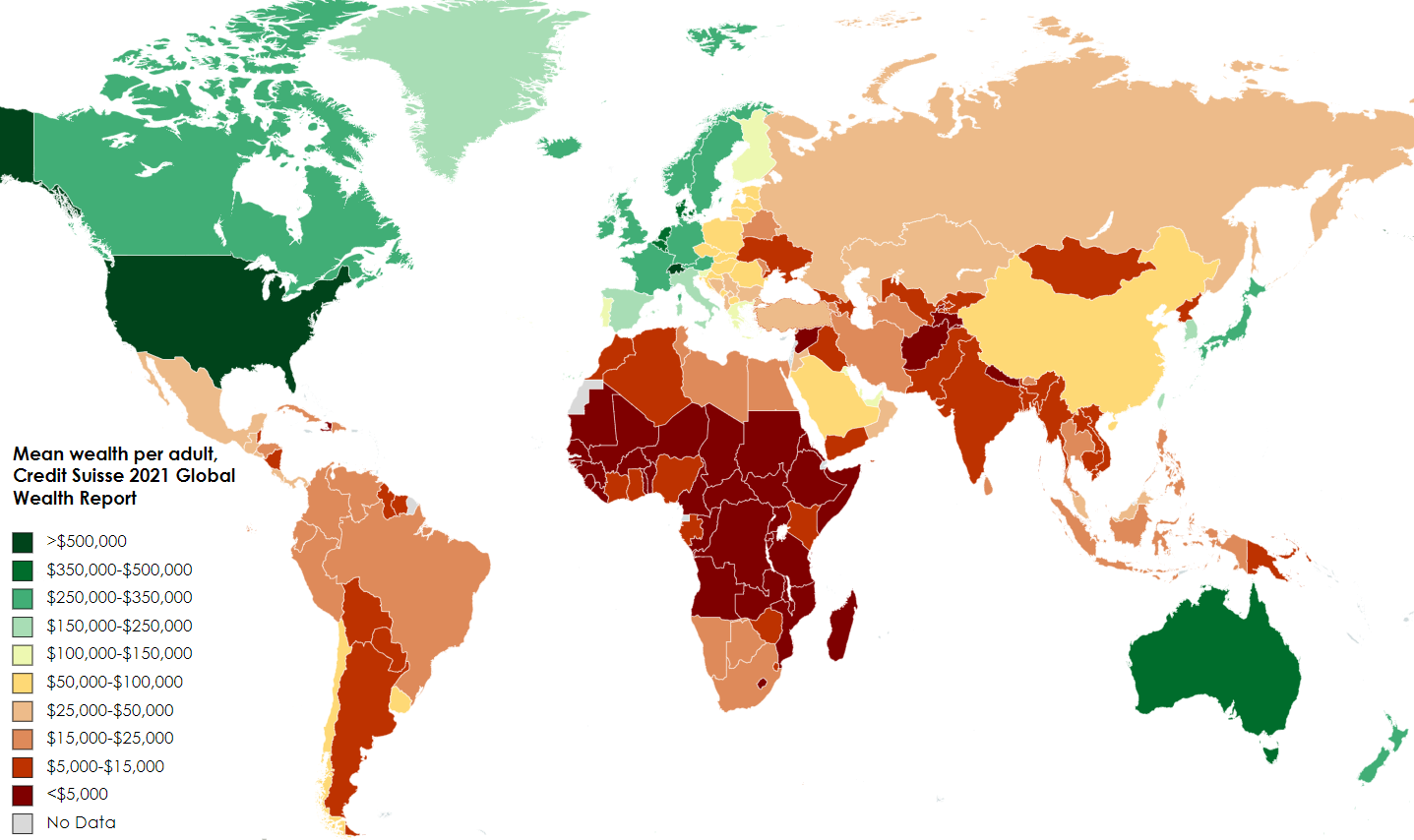 |
💲World Income MapIn 2024, global median incomes show wide disparities across regions. Developed countries, like Luxembourg, rank at the top with median incomes exceeding $26,000 annually, largely due to robust social security systems, high levels of economic stability, and low inequality. Conversely, many lower-income countries, such as the Democratic Republic of Congo, report annual median incomes as low as $400, underscoring significant economic challenges. For instance, while the U.S. has a high median income around $19,000, middle-income countries, including Brazil and India, report much lower levels due to ongoing economic development efforts. Generally, high-income nations enjoy greater financial security, while income inequality remains a concern even in wealthier regions. For more insights into this economic landscape, sources like the World Bank’s Poverty and Inequality Platform provide a comprehensive view of income data. |
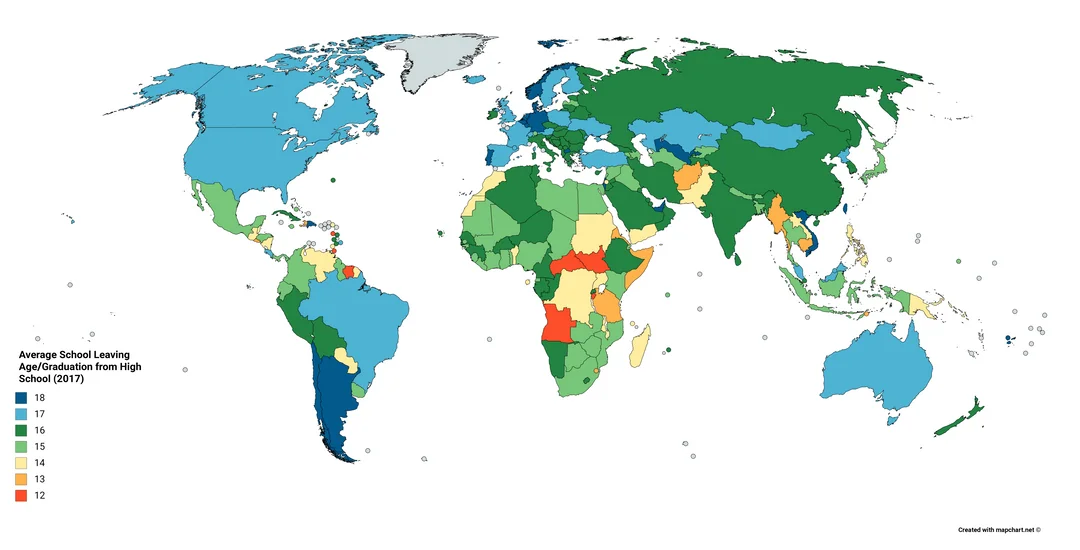
🎓World School Leaving MapThe school leaving age varies around the world, with different countries setting different age requirements for students to complete their compulsory education. In many countries, the minimum school leaving age is 16, including nations like the United Kingdom, France, and most of Europe. However, in some places, students can leave school at an earlier age, such as at 15 in countries like the United States and Thailand. In contrast, countries like Germany and Italy require students to stay in education until they are 18, offering options such as vocational training or apprenticeships during that time. School leaving ages are often influenced by national education policies, economic factors, and cultural norms, and many countries are continually adapting these rules to ensure better educational outcomes. |
 |
 |
❤️🩹World Health MapGlobal health has made strides in recent years, yet faces complex challenges and inequalities that affect outcomes worldwide. Life expectancy has improved in many countries, but this progress is uneven, with high-income nations generally seeing more consistent health advancements. Low- and middle-income countries often grapple with limited healthcare access, significant disease burdens, and lower-quality medical infrastructure. Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like heart disease and diabetes are now a leading cause of death globally, while infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and HIV remain prominent in some regions. Efforts to address these challenges include investments in digital health technology, disease prevention programs, and improvements in health data systems, all aimed at creating a more equitable and resilient healthcare landscape for everyone. |
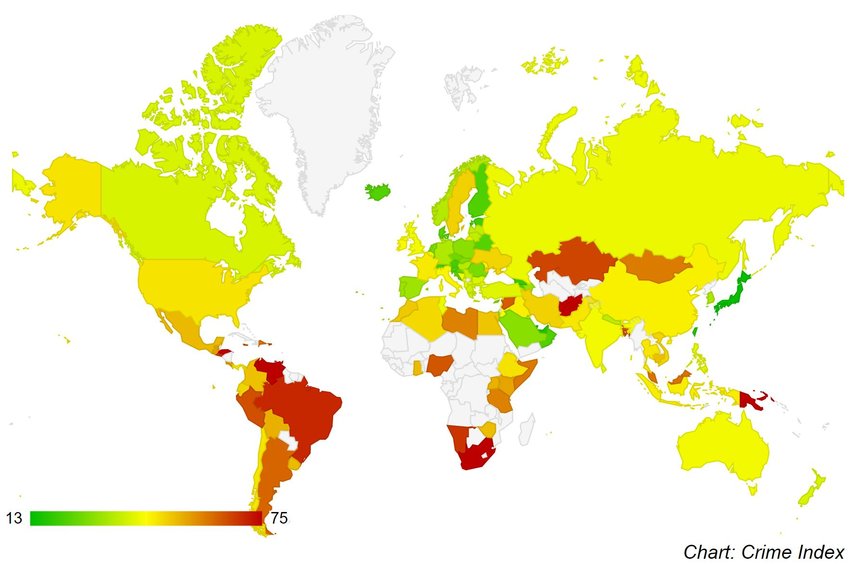
🔪World Crime Rate MapGlobal health has made strides in recent years, yet faces complex challenges and inequalities that affect outcomes worldwide. Life expectancy has improved in many countries, but this progress is uneven, with high-income nations generally seeing more consistent health advancements. Low- and middle-income countries often grapple with limited healthcare access, significant disease burdens, and lower-quality medical infrastructure. Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like heart disease and diabetes are now a leading cause of death globally, while infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and HIV remain prominent in some regions. Efforts to address these challenges include investments in digital health technology, disease prevention programs, and improvements in health data systems, all aimed at creating a more equitable and resilient healthcare landscape for everyone. |
 |
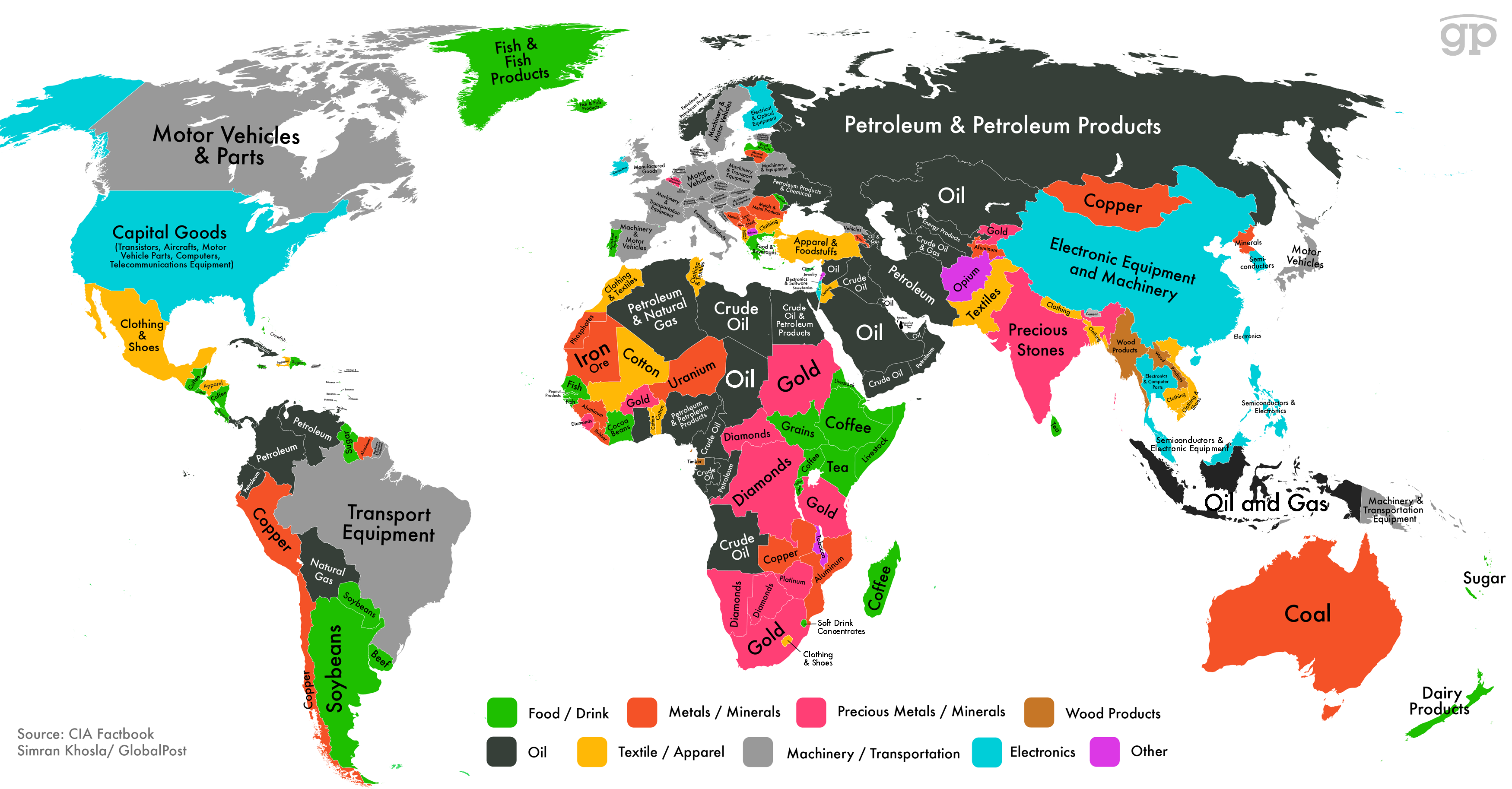 |
📦World Export Products MapThe map highlights the primary export commodities of countries worldwide, reflecting their economic specializations. North America focuses on motor vehicles, capital goods, and clothing, while South America prominently exports petroleum, copper, and soybeans. Africa showcases diversity, with countries exporting diamonds, gold, crude oil, and coffee. Europe leans heavily on machinery, transport equipment, and petroleum products, alongside apparel in certain regions. Asia stands out with electronic equipment, precious stones, and textiles dominating exports, with oil and gas from the Middle East playing a critical role. Oceania contributes coal, dairy products, and sugar. These patterns underline the diverse natural resources, industries, and trade dependencies across the globe. |
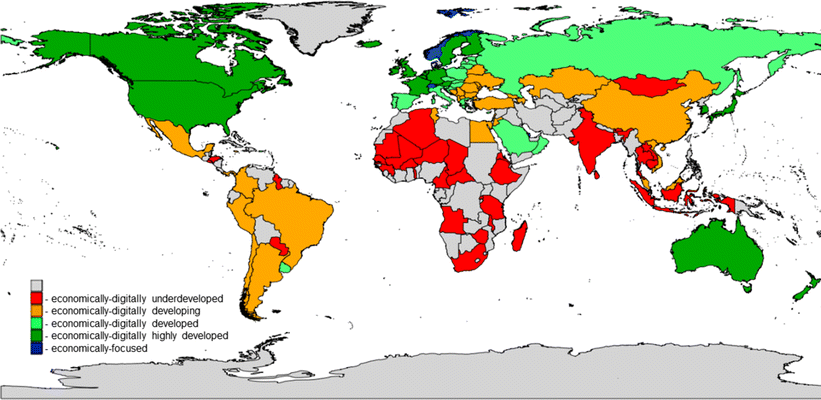
📲Economic and Digital Development Level MapThe map categorizes countries based on their economic and digital development levels. Economically and digitally highly developed nations, marked in blue, dominate North America, Western Europe, and parts of Asia, including Japan and South Korea. Economically and digitally developed countries, shown in green, include regions in South America, Eastern Europe, and parts of Asia. Economically and digitally developing nations, in orange, cover large parts of Africa, South Asia, and Latin America. Economically and digitally underdeveloped countries, marked in red, are concentrated in central Africa and isolated regions worldwide. This visualization highlights disparities in digital and economic growth, reflecting access to technology, infrastructure, and investment across the globe. |
 |