
|
AROUND THE GLOBE |

|
AROUND THE GLOBE |
|
📄About 'Around the Globe'Welcome to Around the Globe! 🌍
Step into the endless wonders of our world with Around the Globe—your ultimate guide to understanding the Earth's diverse landscapes, climates, and cultures. Here, every corner of our planet has a story to tell, from the vast expanses of oceans and the majestic heights of continents to the subtle rhythms of weather zones and time zones. Our website is designed to provide fascinating insights into the natural features that define our world, as well as the unique human creations that shape it. ✒️By Mr. Khaing Min Khant |
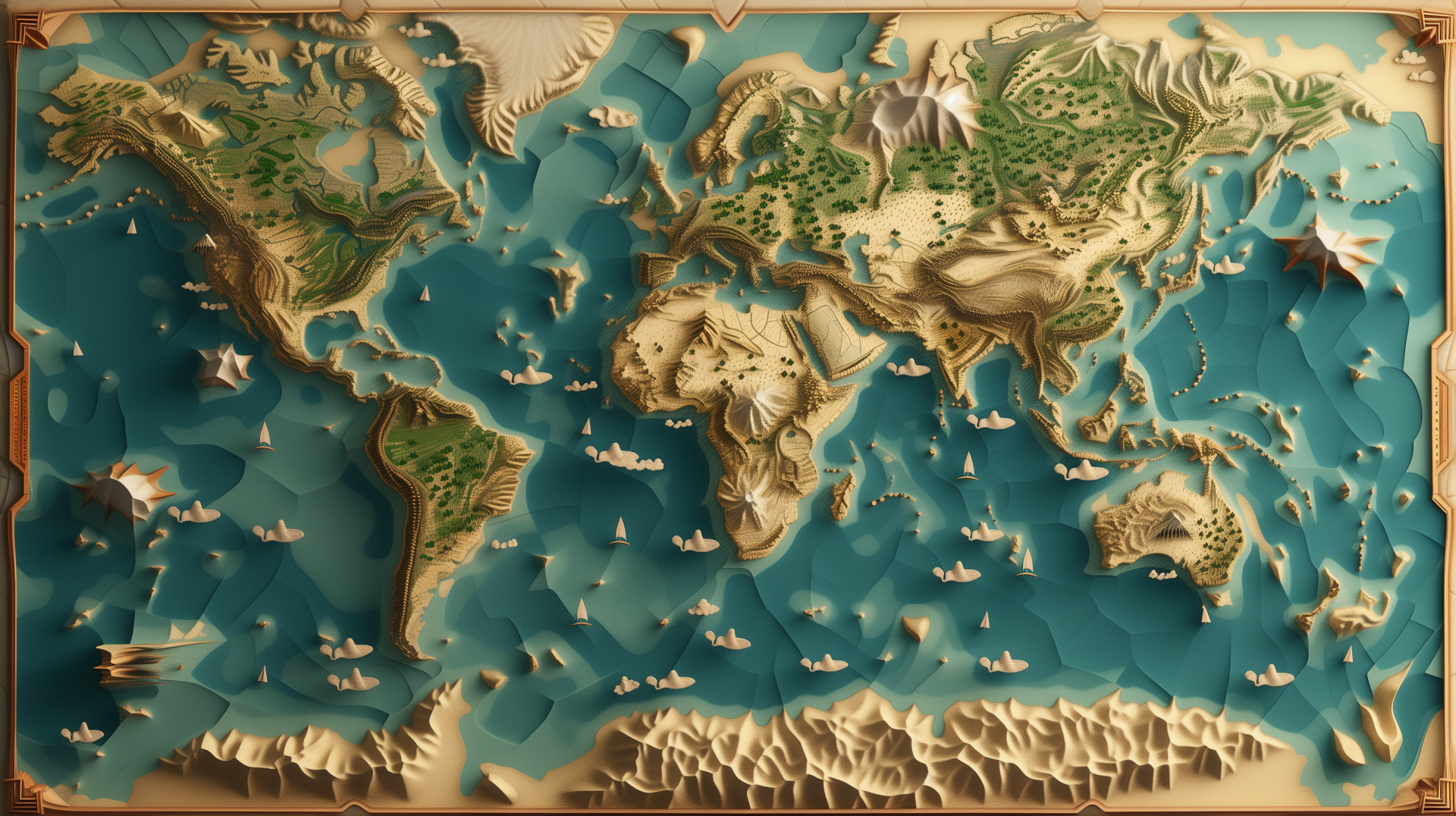
is a remarkable and complex planet that supports an intricate web of life, diverse ecosystems, and a wide range of natural processes. It is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system, and the only one known to harbor life. Earth is approximately 12,742 kilometers (7,918 miles) in diameter, and its surface is divided into two main components: land and water. Around 70% of Earth's surface is covered by water, mainly in the form of oceans, while the remaining 30% is land, which includes continents, islands, and various landforms.
Earth's land is divided into seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. These continents are composed of a wide variety of landscapes and ecosystems, including mountains, forests, deserts, plains, and wetlands. Some regions, such as the Himalayas, boast the tallest mountains on Earth, while others, like the Sahara Desert, are vast expanses of sand and rock. The Earth's surface is constantly reshaped by geological processes, including plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and erosion. These processes can result in earthquakes, mountain formation, and the creation of new landforms. Rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water also shape the planet, providing essential resources for both humans and wildlife.
Earth’s oceans—Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic—cover around 70% of the planet's surface and contain about 97% of Earth's water. These oceans not only provide food, transportation, and resources but also regulate the planet’s climate by distributing heat around the world. Ocean currents play a significant role in climate patterns, influencing everything from weather systems to rainfall distribution. The oceans are teeming with life, from microscopic plankton to the largest animals on Earth, like blue whales. Marine ecosystems such as coral reefs and deep-sea vents are some of the most biologically diverse areas in the world.
|
The Atmosphere and Climate🌦️:Earth's atmosphere is a layer of gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases, that surrounds the planet and makes life possible. The atmosphere is crucial for protecting Earth from harmful radiation from the Sun and helps regulate the temperature, ensuring that the planet remains habitable. The atmospheric pressure is higher at sea level and decreases with altitude, which is why Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth, has less oxygen than areas at sea level. The climate of Earth is driven by the Sun’s energy, and this energy is distributed unevenly across the planet due to the tilt of the Earth's axis and its spherical shape. This causes the seasons and influences global weather patterns. The Earth's climate system includes complex interactions between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and ice, which all contribute to global phenomena such as the water cycle, hurricanes, and monsoons.Biosphere and Life👤:Earth is unique in the universe for its ability to support life. Life on Earth is incredibly diverse, ranging from the smallest single-celled organisms to complex multicellular organisms like humans, plants, and animals. The biosphere, which encompasses all living things, is interconnected and relies on a variety of natural cycles to survive. Photosynthesis, for example, is the process by which plants and certain bacteria use sunlight to create energy, which in turn sustains all other life forms. Food chains and food webs exist throughout ecosystems, from tropical rainforests to the icy waters of the polar regions. Each ecosystem plays an essential role in maintaining the balance of life on Earth.The Challenges of Sustainability💭:In recent years, concerns about the environmental impact of human activities have grown. Issues like global warming, loss of biodiversity, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution are increasingly becoming global challenges. Efforts are being made to create sustainable solutions, including renewable energy sources, conservation programs, and climate change mitigation strategies. The balance between development and environmental protection is one of the most pressing challenges of the 21st century.In summary💡,Earth is an extraordinarily complex planet with a delicate balance of natural processes that sustain life. From its diverse ecosystems and abundant resources to its deep geological layers and atmosphere, Earth continues to be a source of wonder and discovery. However, the increasing pressures from human activity call for a greater understanding of the planet’s systems and a more responsible approach to living in harmony with the natural world.📖📖📖For More Information...📖📖📖 |

"OUR EARTH, there is no heaven, but there are pieces of it!" |
Dear World,Our Earth is a living masterpiece, filled with boundless beauty and endless possibilities, reminding us every day to protect, cherish, and celebrate the incredible home we share. |

|
Continents🏝️Our Earth is divided into seven vast landmasses known as continents, each uniquely diverse in its geography, climate, ecosystems, and cultures. These continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia —cover approximately 30% of the planet's surface, with the rest enveloped by oceans. Asia, the largest, is home to a vast array of landscapes, from towering mountain ranges like the Himalayas to expansive deserts and dense rainforests. Africa, celebrated for its rich wildlife and history, offers deserts like the Sahara and dense forests along the equator. North and South America stretch across both northern and southern hemispheres, boasting ecosystems ranging from the Amazon Rainforest to the Rocky Mountains. Antarctica, the southernmost continent, remains largely uninhabited due to its icy conditions but plays a crucial role in Earth’s climate. Europe and Australia, though smaller in size, are culturally significant and ecologically rich, with Europe known for its varied climates and dense human history, while Australia is celebrated for its unique wildlife and outback landscapes. Together, these continents make up the intricate and interdependent global landscape that sustains diverse forms of life and fosters a multitude of human cultures. 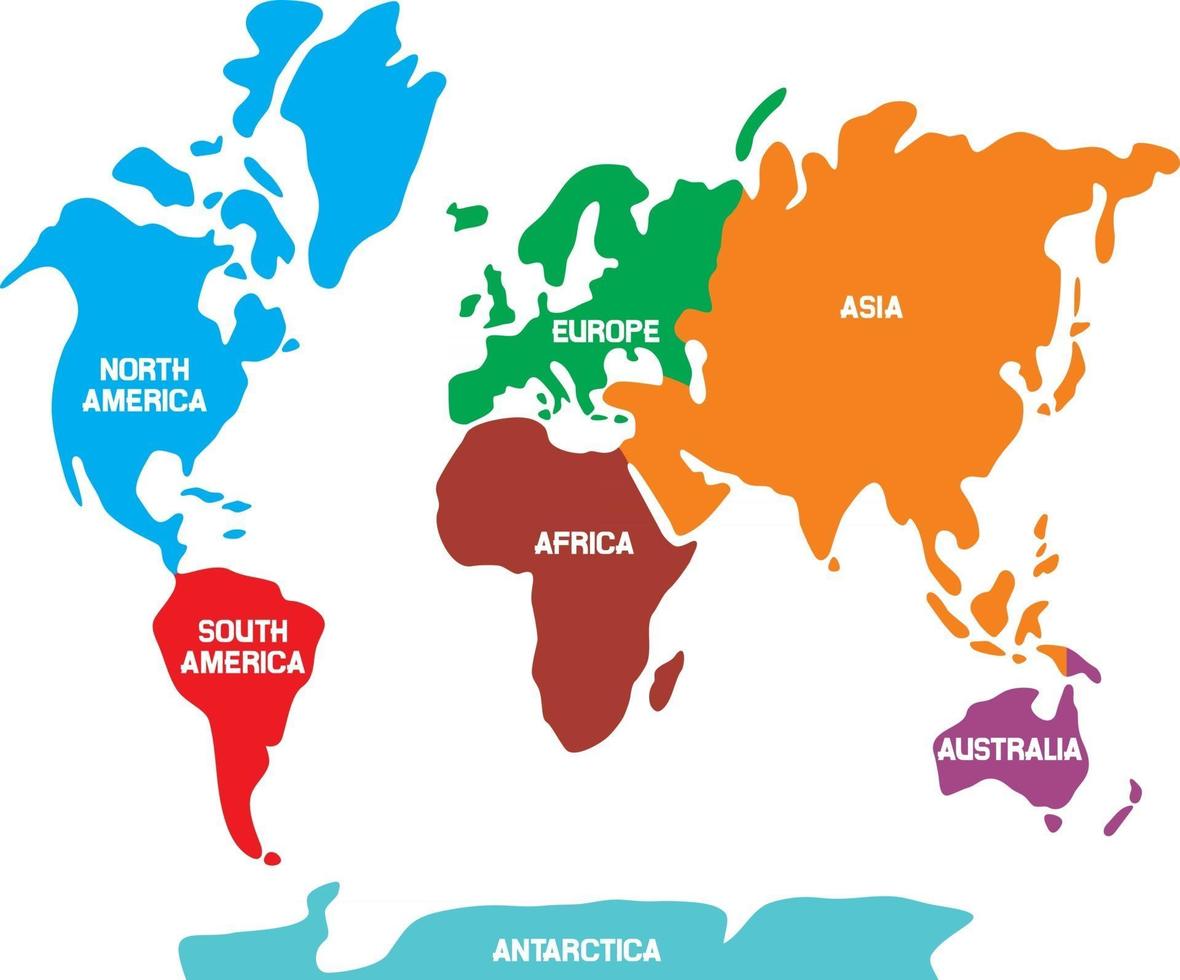
|
|
Oceans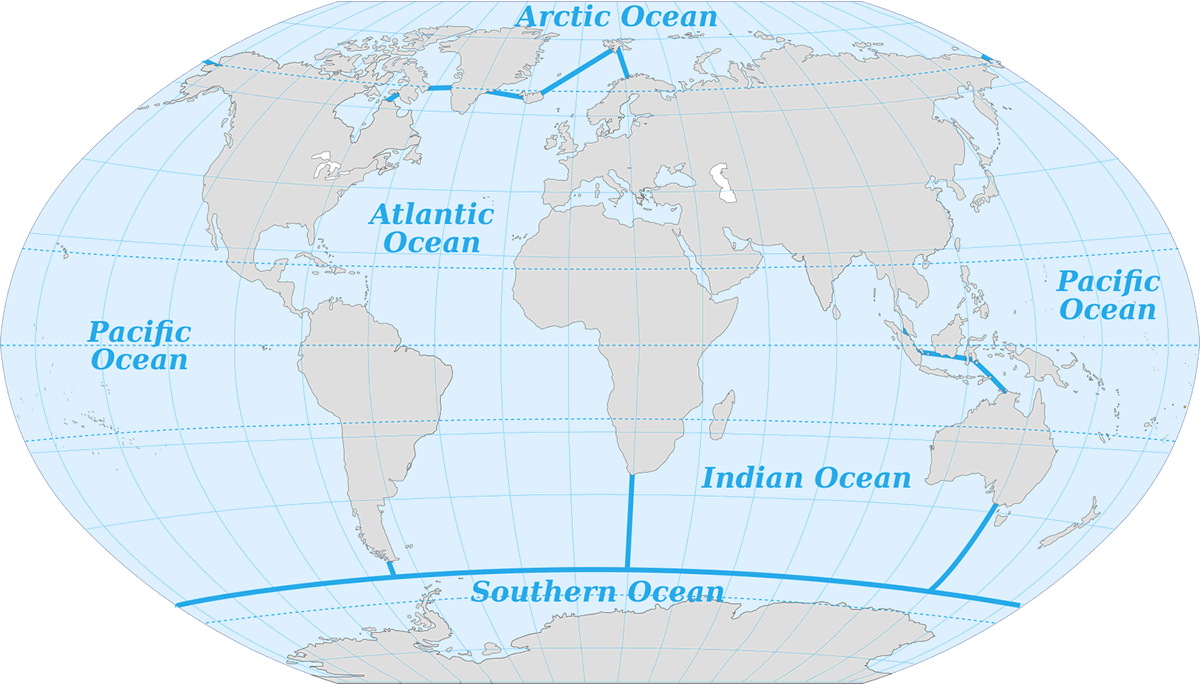
🛳️Oceans cover around 70% of Earth's surface, forming vast, interconnected bodies of saltwater that play a critical role in supporting life, regulating climate, and shaping weather patterns. Our planet has five primary oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic. The Pacific Ocean, the largest and deepest, stretches from the Americas to Asia and Oceania, housing diverse marine life and ecosystems within its coral reefs, trenches, and islands. The Atlantic Ocean, known for its rich history of exploration, spans between the Americas and Europe and Africa, influencing the climates of coastal regions and supporting major fisheries. The Indian Ocean, warm and biodiverse, borders Asia, Africa, and Australia and is vital to trade routes and monsoon patterns. The Southern Ocean, encircling Antarctica, plays a key role in regulating Earth’s temperature by driving global currents and supporting cold-adapted species. Lastly, the Arctic Ocean, the smallest and shallowest, is surrounded by the northernmost continents and significantly impacts global weather and climate. Together, these oceans form a complex, interlinked ecosystem essential to life on Earth, shaping the planet’s natural cycles and serving as a foundation for a rich diversity of marine species. |
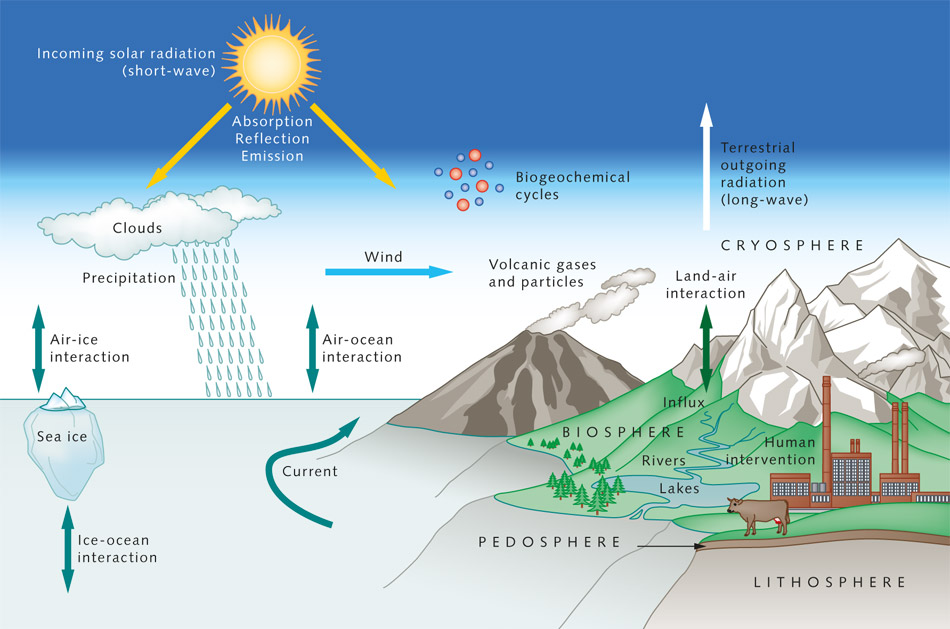
|
Earth’s climate🔥 is a complex and dynamic system influenced by a variety of interconnected factors. Climate includes long-term weather patterns, encompassing temperature, precipitation, humidity, and wind. It varies across different regions of the globe, creating diverse environments from lush rainforests to vast deserts. Understanding Earth’s climate is crucial for grasping the delicate balance that supports life and assessing the impact of human activity on this system. |
|
|
🎥Climate Change Short Film🎥 |

|
Earth is an extraordinary planet, bursting with life in forms as varied as microscopic bacteria, colorful coral reefs, and intelligent humans. It is a perfect stage for life, with its unique combination of water, atmosphere, and climate. The biosphere, the layer of Earth that supports life, is a complex web of interactions between organisms and their environments, sustaining the planet’s ecosystems. Living organisms inhabit nearly every part of Earth, from the deepest trenches of the oceans to the highest mountain peaks, thriving in conditions as extreme as arid deserts or freezing polar regions. Each species plays a vital role in its ecosystem, whether it’s a tiny plankton producing oxygen in the oceans, a predator controlling prey populations, or decomposers breaking down organic matter to recycle nutrients back into the soil. 💬Earth is a thriving sanctuary where all living things inspire and flourish. |
💡SummaryEarth is a vibrant planet teeming with diverse life forms, each playing a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. However, human activities threaten this balance, leading to biodiversity loss and disrupting the planet’s natural resilience. Understanding and preserving Earth’s living systems is crucial for the survival of all life forms. |

🧓HumansHumans are undoubtedly the most dominant species on Earth, having the unique ability to think critically, innovate, and adapt to almost any environment. Unlike other living organisms, humans have transformed their surroundings to suit their needs by building cities, cultivating crops, and advancing technology. While these achievements have improved living standards, they have also led to major environmental challenges. Deforestation, pollution, overfishing, and the burning of fossil fuels have disrupted ecosystems and endangered countless species. Despite these challenges, humans possess the power to protect and restore the natural world. Through conservation efforts, technological advancements, and global cooperation, humanity has the potential to mitigate the damage caused to the environment and ensure the survival of other species. At the heart of it all, humans are not just stewards of the planet but are deeply dependent on the ecosystems they influence, making their role in Earth's biosphere both impactful and precarious. |

🐂AnimalsAnimals are among the most fascinating and diverse living organisms on Earth, ranging from the smallest insects to the largest mammals. Vertebrates, such as mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, are often the most familiar, while invertebrates like insects, spiders, and mollusks make up the majority of animal species. Animals play a crucial role in ecosystems by maintaining balance through predation, pollination, and nutrient cycling. For example, bees pollinate crops, enabling the growth of food that sustains humans and other species, while predators like lions control herbivore populations, preventing overgrazing. Marine animals, from tiny plankton to massive whales, are vital for ocean ecosystems, which regulate global climate and provide food for millions. Despite their importance, many animal species face extinction due to habitat loss, climate change, and poaching. Protecting animals and their habitats is essential not only for their survival but also for the health and stability of ecosystems worldwide. |

|
🍃PlantsPlants are the cornerstone of life on Earth, serving as the primary producers that sustain almost all other living organisms. Through the remarkable process of photosynthesis, plants convert sunlight into energy, producing oxygen as a byproduct—an essential element for most life forms. They form the base of the food chain, providing sustenance directly to herbivores and indirectly to carnivores. Plants are incredibly diverse, ranging from tiny mosses and algae to towering redwoods and sprawling tropical rainforests. These green organisms thrive in nearly every environment on Earth, from arid deserts where cacti store water to aquatic ecosystems where seaweed anchors marine food chains. Forests, often called the "lungs of the planet," play a critical role in regulating the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. |

|
The Earth faces significant challenges that threaten its future stability. Rising global temperatures have increased by over 1°C since pre-industrial times, contributing to severe climate changes. Deforestation claims around 10 million hectares of forest annually, endangering biodiversity. Over 8 million metric tons of plastic enter the oceans each year, harming marine life. The human population, now exceeding 8 billion, places immense pressure on natural resources. Additionally, nearly one-third of the world's soil is degraded, reducing agricultural productivity and food security. Addressing these issues requires urgent global cooperation and innovative solutions. |
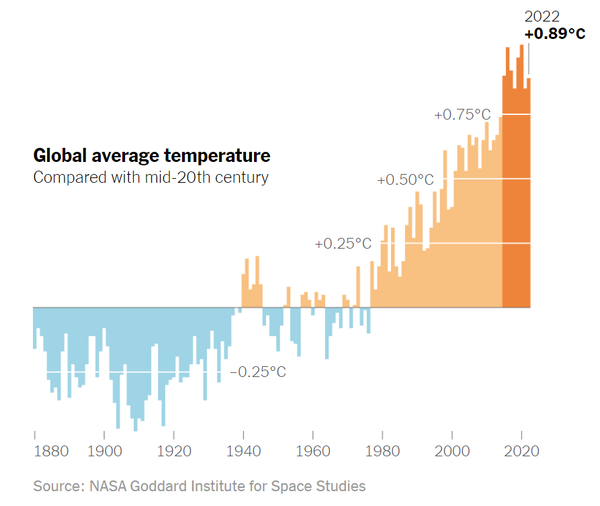
🌡️Rising Global TemperaturesGlobal temperatures have increased by over 1°C since pre-industrial times, leading to drastic climate changes. This warming has intensified natural disasters such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and droughts, impacting ecosystems and human livelihoods. Polar ice caps are melting at alarming rates, causing sea levels to rise and threatening coastal communities. Without significant action, these trends will continue to endanger the planet's balance. |
🪓DeforestationEach year, approximately 10 million hectares of forest are lost due to deforestation. This widespread destruction is driven by agriculture, logging, and urban development. Forests, which act as carbon sinks and house countless species, are vital to maintaining Earth's biodiversity and climate stability. The loss of forests not only accelerates climate change but also disrupts ecosystems and the livelihoods of millions who depend on them.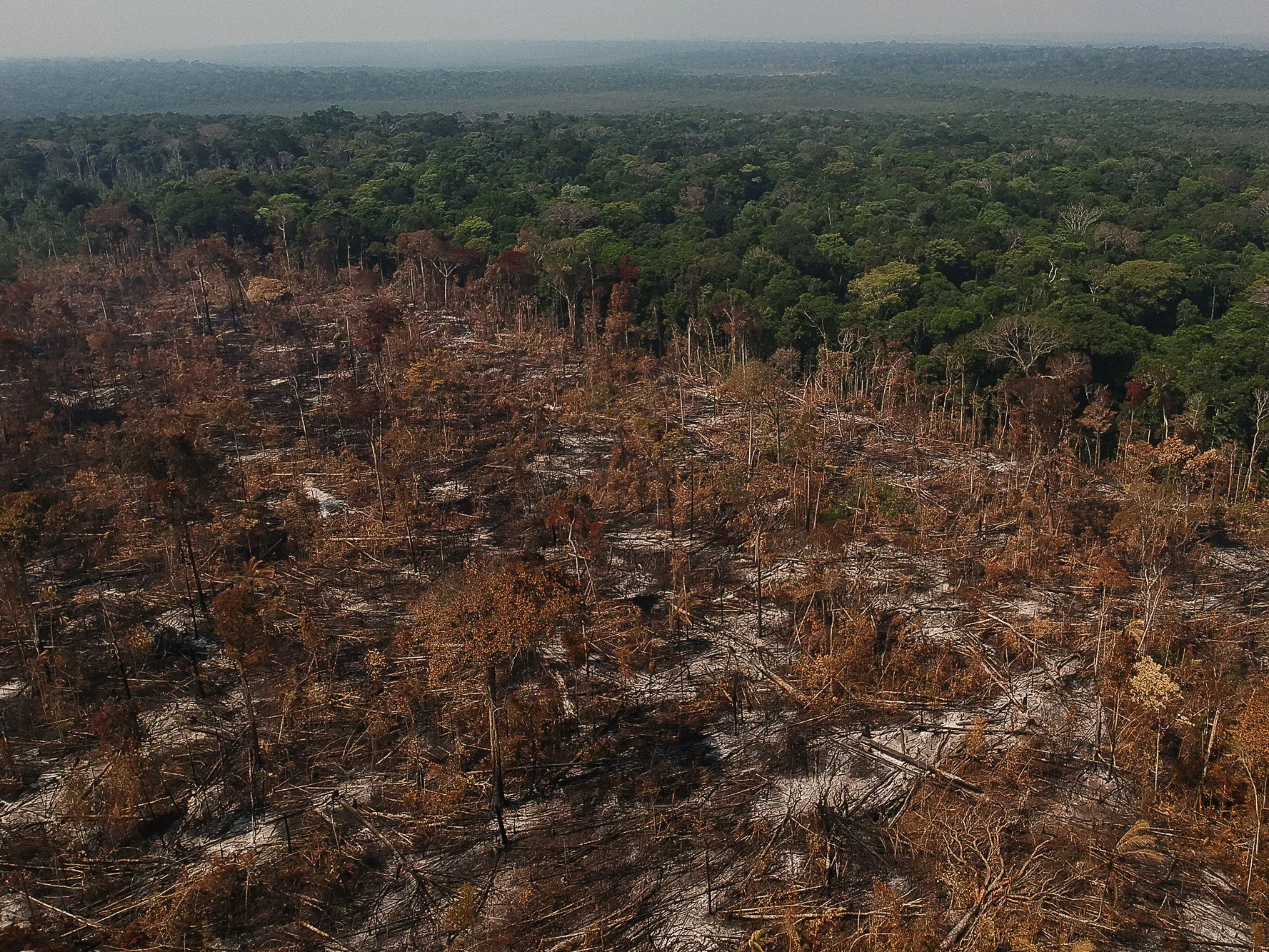 
|
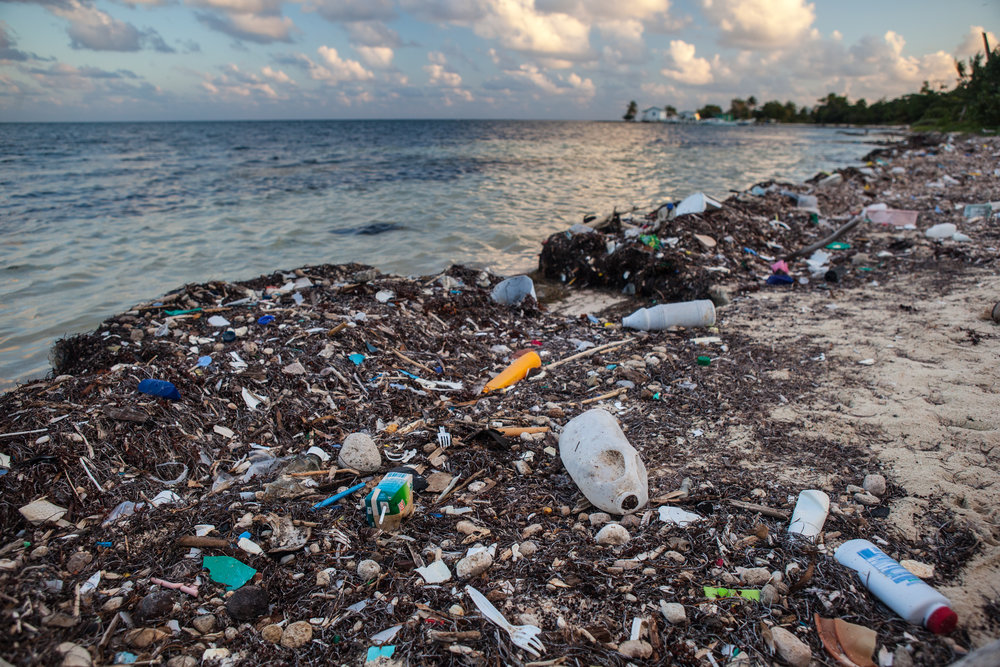

♻️Plastic Pollution in OceansOver 8 million metric tons of plastic end up in the oceans annually, posing a severe threat to marine life. Animals often mistake plastic for food, leading to starvation, injury, or death. Microplastics have infiltrated the food chain, affecting humans as well. Oceanic plastic pollution also damages coral reefs and degrades the beauty of natural marine environments. Reducing plastic waste is essential to protect our oceans and their inhabitants. |
👤Human Population PressureWith the global population now exceeding 8 billion, the demand for resources has reached unprecedented levels. This rapid growth strains food production, water supplies, and energy systems. Urbanization expands into natural habitats, furthering environmental destruction. To ensure a sustainable future, it is crucial to balance population growth with resource conservation and equitable distribution.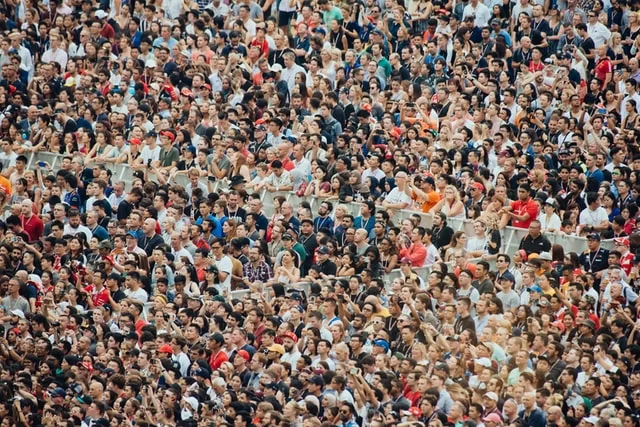 
|
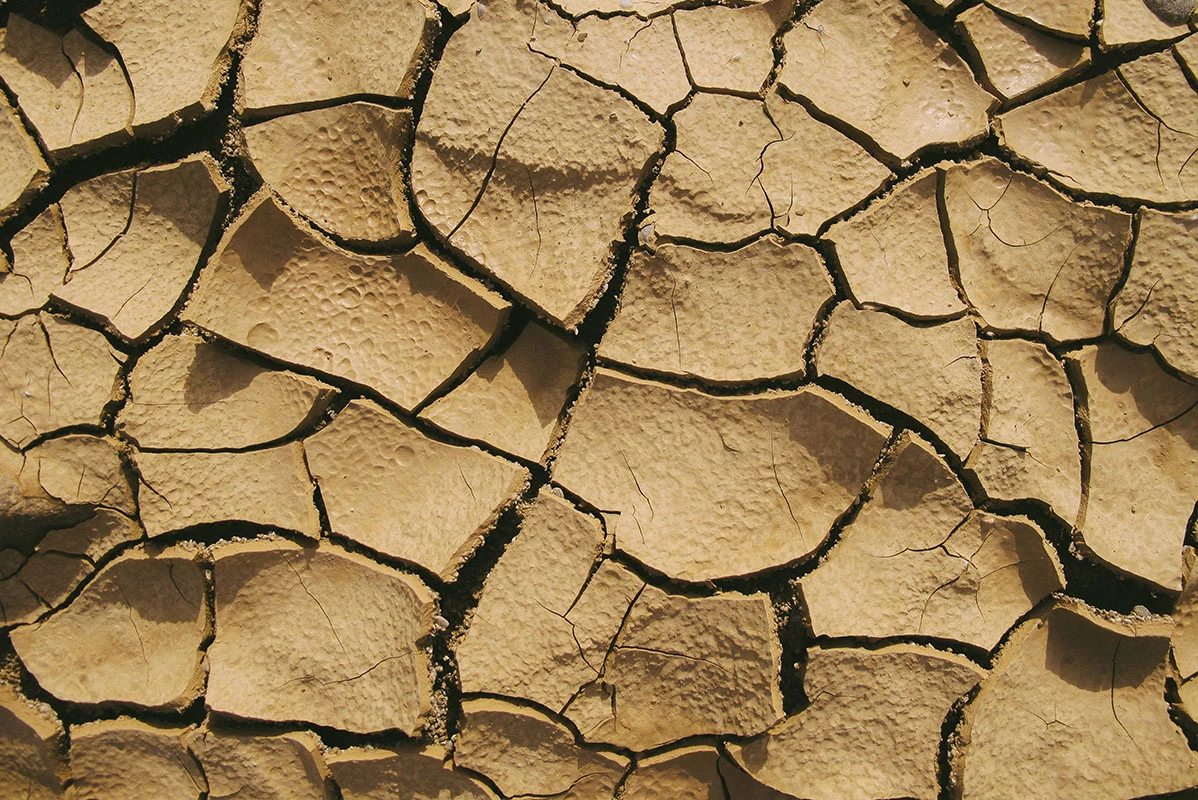

🌱Soil DegradationWith the global population now exceeding 8 billion, the demand for resources has reached unprecedented levels. This rapid growth strains food production, water supplies, and energy systems. Urbanization expands into natural habitats, furthering environmental destruction. To ensure a sustainable future, it is crucial to balance population growth with resource conservation and equitable distribution. |
📖Summary📖
Earth, our home planet, is a dynamic and uniquely diverse world within the vast cosmos. It is the third planet from the Sun and the only known celestial body that supports life. With a radius of approximately 6,371 kilometers, Earth is the fifth-largest planet in the Solar System and stands out for its blue appearance from space, largely due to its extensive oceans that cover about 71% of its surface. The remaining 29% consists of continents and islands, forming diverse landscapes such as towering mountains, sprawling deserts, dense forests, and fertile plains. This intricate blend of land and water has given rise to a remarkable variety of ecosystems and life forms. Earth's atmosphere, composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), plays a critical role in sustaining life by regulating temperature, protecting the surface from harmful solar radiation, and providing essential gases for respiration and photosynthesis. |

|

|
|||||
Climate🌦️Earth’s climate system is another defining feature of its uniqueness. Powered by solar energy, the climate varies widely from the freezing poles to the scorching deserts and temperate zones. Weather patterns and climates are influenced by the atmosphere, oceans, and the biosphere in a delicate balance. These systems interact to regulate temperature, precipitation, and seasonal changes, enabling life to thrive in various forms and adaptations. However, this balance is increasingly threatened by human activity, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, which contribute to global warming, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events. Protecting this intricate balance is critical to ensuring a sustainable future for all life on Earth. |
Living Things🦥Beyond its natural beauty and ecological significance, Earth is a cradle of human civilization. Over millennia, humans have developed diverse cultures, languages, and technologies, profoundly shaping the planet. While Earth's resources have enabled remarkable achievements, from agriculture to space exploration, they are finite, urging humanity to adopt sustainable practices. International efforts like climate agreements and conservation initiatives highlight the growing awareness of our collective responsibility to protect our planet. |
Summary💡In essence, Earth is more than just a planet; it is a living, breathing system teeming with complexity and wonder. From the microscopic to the cosmic scale, it is a reminder of the delicate interplay of forces that make life possible. As stewards of this incredible planet, it is our duty to cherish and protect it for future generations, ensuring that its natural beauty and resources remain a source of life and inspiration. |
|||